Treatment & Approaches For Stroke
Interventional or Minimal Invasive Approach
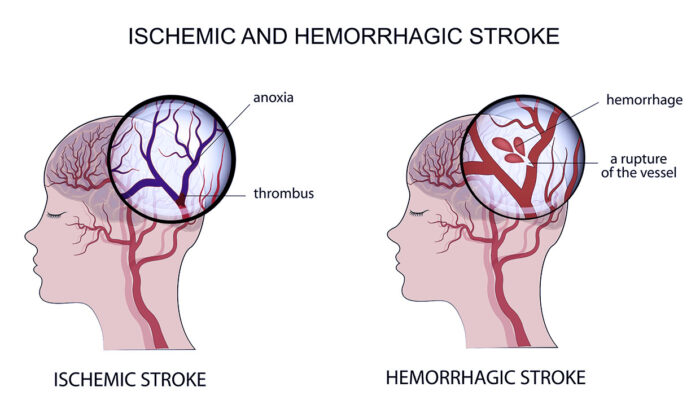
In the event of ischemic stroke, the first line of treatment is to dissolve or remove the blood clot. If a stroke is diagnosed quickly enough, a clot-busting medications can be given. If possible, a catheter can be used to remove the clot in a procedure called an embolectomy. In some cases, angioplasty and stenting are used to widen an artery and keep it open.
Such type of interventional procedure is always done in a CATHLAB and not in operation theatre and is operated by interventional radiologist or neurologist so before rushing to a hospital check whether the hospital has both OT and CATHLAB.
At Jinkushal hospital we have a CATHLAB and Operation theatre alongside to manage any type of complications, the specialty of this CATHLAB is that it has inbuilt CT scan so in case of emergency we do not waste time transferring the patient for CT scan and the procedure is done with precision and reduces the chances of complications.
Surgical Approach
For a hemorrhagic stroke, the bleeding must be stopped. In this surgical approach the skull is opened surgically (craniotomy) to release the pressure. And if the stroke was due to aneurysm then a clip is sometimes placed on the aneurysm to stop the bleeding. Medication to reduce clotting also may be required.
In the meantime, your medical team may need to take additional measures to keep your heart and lungs functioning.
Long-Term Outlook
A brain stem stroke can result in serious long-term problems. Medication and ongoing therapy may be necessary. Physical therapy can help people regain large motor skills and occupational therapy can help with everyday tasks.
Speech therapy can help you regain control over how you speak and swallow.
Some survivors of brain stem stroke are left with severe disabilities. In these cases, psychological counseling can help them adjust.
Preventing Stroke
Despite the risks that you can’t avoid, there are things you can do to decrease your chances of stroke. Some general guidelines to follow include:
• Eat a low-fat and low-sodium diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fish.
• Exercise regularly.
• Don’t smoke.
• Don’t abuse alcohol or drugs.
If you’re obese or have high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, or a type of chronic illness, follow your doctor’s recommendations for keeping them under control.
If you or someone around you experiences any of these warning signs, don’t wait. Call emergency services immediately. Even if symptoms seem to improve or disappear, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly, as transient symptoms can still indicate a serious underlying condition like a mini-stroke (transient ischemic attack) that requires medical evaluation and treatment.
At Jinkushal Cardiac Care & Superspeciality Hospital, we have a team of highly experienced Neurologists and Neurosurgeons who are experts in handling any emergency stroke situation.